All but Which of the Following Describe the Reticular Formation
Pain filtering inputs - ascending - for arousal and attention medial zone. It is responsible for arousal to keep the cortex conscious and alert via RAS c.

Reticular Formation And Limbic System Textbook Of Clinical Neuroanatomy 2 Ed
- reticulospinal tract descends from the pontine reticular formation down the medial longitudinal fasciculus and then in the anterior funiculus of the spinal cord.

. Start studying the Reticular Formation flashcards containing study terms like Where does the reticular formation extend Neurons within the reticular formation have what functions The ascending portion of the reticular formation is called what. Correctly label the following figure representing the reticular formation Radiations to cerebral cortex Auditory input Thalamus Visual input Reticular formation Prey 6 of 50 Next 9 MB acer 2 95 5 3 7 8 9 W e у u 0. What is the location of the reticular formation.
Midline Reticular Formation contains Raphe Nuclei Serotonin medial reticular formation -Ascending descending projections. The dendrites and axons of the reticular formation are atypical when compared to those of other neurons. Its functions can be classified into 4 categories.
Function of the reticular formation. The nerve fibers in these pathways act in the spinal cord to block the. The dendrites are polysynaptic giving rise to the reticular formation being described as a non-specific unit.
Cardiovascular control The reticular formation includes the cardiac and vasomotor centers of the medulla oblongata. The axons are extremely long and can reach sites far removed from their cell bodies. The reticular formation is a complex network of brainstem nuclei and neurons that serve as a major integration and relay center for many vital brain systems to coordinate functions necessary for survival.
Motor control sensory control visceral control and control of consciousness. Spaces in the brainstem that are not occupyed by cranial nerve nuclei and there tracts. All but which of the following describe the reticular formation.
Check all that apply. What are the major functions of the reticular system. Neuroanatomy Reticular Formation - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf.
Modulation of pain transmission control of movement including conjugate eye saccades autonomic reflexes arousal and consciousness. The structure of the reticular formation forms a net-like connection of nuclei and neurons hence its. What are the seven major functional groups of the reticular nuclei.
E screens irrelevant visual and auditory information. Associated with diffuse modulating systems 6. Some descending pathways from the reticular formation.
It regulates visceral motor functions via. Conduction and modulation of slow pain 5. In is the Substantia Nigra.
A diffuse collection of neurons that extend through the central core of the brainstem from medulla to midbrain. Influence voluntary movement 3. Which of the following statements about the reticular formation is false.
Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. Pathways originating in the raphe nuclei in the midline of the brainstem. Anatomy and Physiology questions and answers.
It is also the origin of the descending analgesic pathways. What is the reticular formation. It passes through the medulla pons and stops in the midbrain.
The neurons have large dendrites that extend long distances to receive and integrate synaptic input from almost all of the axons that project to or through the brainstem. The reticular formation is a nerve network of nuclei clusters found in the human brain stem. It filters in 99 of all stimuli via ascending reticular formation d.
Associated with respiration 7. A net-like structure made up of several nuclei and tracts is known as reticular formation. It is primarily responsible for visual perception.
Regulate sleep arousal and wakefulness. Today the reticular formation is considered to play a very important role in different activities of the brain and the nervous system. Aminergic neurones release one of the following amines at the terminals.
Role in sleep and wakefulness cycle It plays a central role in states of consciousness like alertness Controls muscle tone Role in visceral function Influences EEG Influences learning Influ. The best which describes the reticular formation of the brain is. It is the master endocrine gland of the brain.
It arises from the brain stem and has wide-ranging axonal connections b. One-thousandth of a second. 1 medial reticulospinal pontine.
Besides acting as mechanical barriers the skin and mucosae of the body contribute to body protection in other ways. After a neuron fires about how long is its refractory period. - Midline raphe nuclei - Medial zone magnocellular gigantocellular nuclei - Lateral zone parvocellular reticular nuclei raphe on midline - neurons contain serotonin - modulatory - Facilitatory or inhibitory eg.
A contains nerve pathways that connect the hindbrain with the forebrain. The correct answer is - All the given options are correct A- The reticular formation is responsible for the ability to stand up straight. 3 Which of the following is a true statement regarding the reticular formation.
The reticular formation is a neuron network in the brainstem that enables consciousness sensory and motor function and endocrine and neurotransmitter regulation. Phineas gage showed severe personality changes following an accident that damaged him. All but which of the following describe the reticular formation.
Reticular Formation a nerve network in the brainstem that plays an important role in controlling arousal Cardiovascular Respiratory Reflex Wakefulness. Regulate visceral activity via autonomic nervous system 4. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high.
What are the 3 sections of the reticular formation. -Motor Functions -Magnocellular Nuclei Lateral Reticular Formation. This part of the central nervous system spread in three main columns from one end of the brainstem to the other is a core relay point that connects the nerves of the spinal cord with.
Memorize flashcards and build a practice test to quiz yourself before your exam. It is mainly involved in motor coordination and balance. Cite the common body locations and the importance of mucus lysozyme keratin acid pH and cili.
Pain modulation The reticular formation is one means by which pain signals from the lower body reach the cerebral cortex. The structure of this formation is highly complex but organized. Incluence CN output 2.
Both efferent and afferent fibers interact with the reticular formation to. The reticular formation is a portion of the brain that is located in the central core of the brain stem. Motor control refers to physical movements or.
Reticular formation as the name suggests is a network of neurons and nerve fibers present in the brain. The dorsal tegmental nuclei are in the midbrain the central tegmental nuclei are in. B- The reticular formation aids the ability to cat.
Earlier no particular function was known to be associated with the reticular formation. View the full answer.
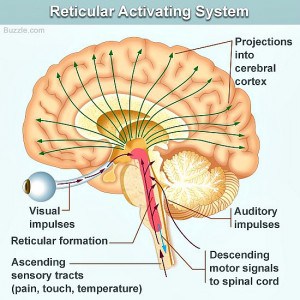
Meet The Reticular Activating System Ras Unyte Integrated Listening
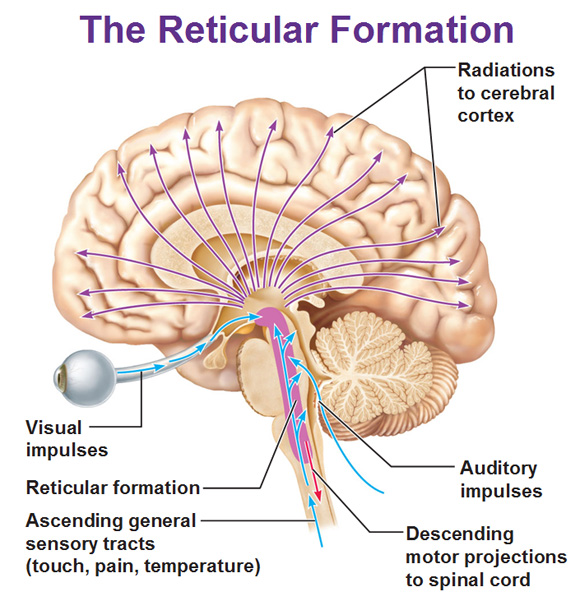
The Limbic System And The Reticular Formation

Reticular Formation Definition Functions Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Reticular Formation Function Location What Is The Reticular Formation Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
No comments for "All but Which of the Following Describe the Reticular Formation"
Post a Comment